. can be defined first aid It is defined as providing immediate care to a person suffering or injured as a result of a non-life-threatening injury or the onset of an illness until medical assistance arrives. For example, providing CPR to revive a person until specialized medical assistance (paramedics) arrives at the scene is a classic example of first aid.

The goal of first aid is to provide the necessary care to prevent serious injury by managing the injury as quickly as possible before receiving specialized medical assistance.
Recognizing the seriousness of the situation is crucial in determining the type of care needed. It is helpful to call 911 and stay on the line if you suspect a serious illness or injury.
First Aid Kit Essentials
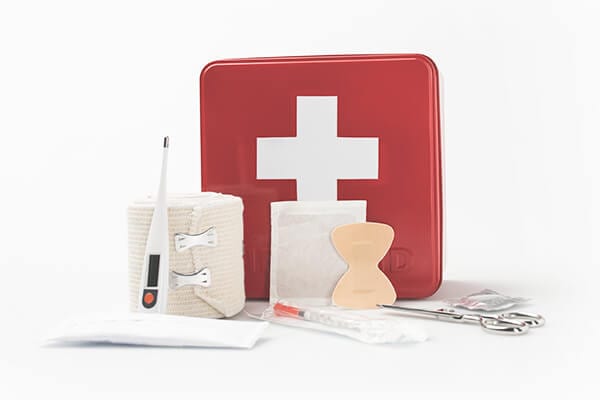
ought to First aid kit includes Ideally the following items:
- Bandages of different sizes
- Roll bandages
- tape
- sterile gauze
- disinfectant wipes
- disinfectant swabs
- Antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide)
- eye ointment
- eye wash
- CPR mask
- non-rubber gloves
- antibiotic ointment
- 0.5% or 1% hydrocortisone cream
- Calamine lotion
- Thermometer
- Acetaminophen
- Ibuprofen
- God
- Disposable cold compresses
- Flashlight with extra batteries
- a pair of scissors
- tweezers
- First Aid Phone Directory
First aid for minor cuts or scrapes
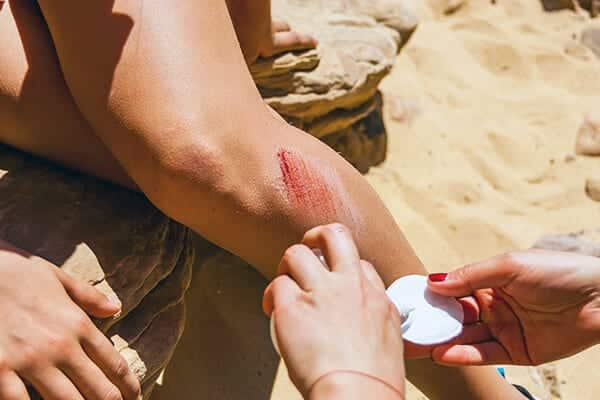

Prompt treatment of an open wound helps reduce the risk of scarring and infection. Here's what you should do immediately after a cut, scrape, wound, or other open injury:
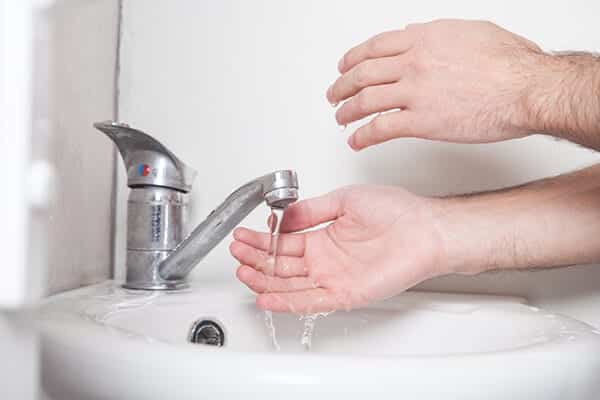
- Wash your hands before treating any cuts or scrapes to prevent bacteria from entering open skin and reduce the risk of infection.
- Control bleeding. Bleeding usually stops soon after the injury. If the bleeding doesn't stop soon afterward, apply pressure to the wound with gauze or a clean cloth and elevate it until the bleeding stops.
- Clean the wound immediately. Running water over a minor cut or scrape can eliminate the risk of infection. Using soap, gently and thoroughly wash the edges of the wound. Do not insert soap into the wound. Sterile tweezers can be used to remove any dirt or debris from the wound. If all the dirt cannot be removed, seek professional medical help.
- Apply antibiotic ointment or petroleum jelly. This moisturizes the wound surface and prevents scarring. If a rash occurs after applying antibiotic ointment, discontinue use.
- Apply a bandage. Cover the wound with a bandage made of sterile gauze and paper tape. Covering the wound keeps it clean and protects it from infection.
- Dress the wound frequently. To protect the wound, it must be kept clean; therefore, it is essential to reapply the dressing at least once a day. If the dressing becomes soiled or wet in any way, change it as soon as possible.
- Get a tetanus shot. A tetanus shot is necessary if it has been more than five years since your last dose. Additionally, if the wound is deep and dirty, seek medical advice about a possible tetanus shot.
- Watch for infection. If you notice any warmth, swelling, drainage, or pain near the injury site, talk to your local healthcare provider to determine the best treatment options for your needs.
- Seek professional medical help. Depending on the depth and location of the wound or cut, you may need to visit the emergency room or doctor to have the injury cleaned and closed (stitches/staples).
Stop nosebleeds at home
Nosebleeds are common, so knowing what to do when they occur can be very helpful.
Here are the steps to stop a nosebleed:
- Sit upright and forward. An upright, forward position can be helpful in treating a nosebleed immediately. Sitting upright reduces blood pressure in the nasal veins, effectively controlling nosebleeds.
- Lean forward. This prevents swallowing blood, which can irritate the stomach lining and cause additional discomfort.
- Gently blow your nose. This can dislodge debris and blood clots, making breathing easier. Then, spray a nasal decongestant containing oxymetazoline into each nostril.
- Pinch your nose. For 10-15 minutes, use your index finger and thumb to gently pinch your nose and breathe through your mouth. Pinching can stop a nosebleed by increasing pressure on your nasal septum. If bleeding persists, pinch your nose again for another 10-15 minutes. If bleeding continues, seek professional medical help.
First aid for animal bites and stings

bites Animal stings release certain toxins into the body that lead to: allergic reactionSome common symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism are: Allergy Type 1/Allergic reaction to an animal bite or sting is:
- itchy skin
- Edema
- Runny nose
- whistling
- breathing difficulties
- abdominal cramps
- Anaphylactic shock in severe cases
Here's what to do immediately after being bitten or stung by an animal or insect:
- Temporarily move to a safer location where the source of bites and stings is limited.
- If visible, remove the stinger. This can be done using a pair of tweezers.
- Immediately use soap and water on the affected area.
- Use an ice pack, cold compress, or cold washcloth on the site of the bite or sting. Doing so will reduce pain and subsequent swelling. Do not apply ice directly to the wound, as it can further damage your skin and may even cause FrostbiteFor the same reason, do not apply an ice pack to the wound for extended periods.
- If the bite is on an extremity, elevate the affected extremity.
- Several times a day, apply calamine lotion, 0.5% or 1% hydrocortisone cream, or baking soda paste to the bite until symptoms improve.
- If itching occurs, antihistamines such as Benadryl lotion may be helpful.
Treating minor burns
minor burn It is any burn less than 8 cm (3 inches) in diameter and is usually characterized by pain and blisters.
Here are some first aid measures for dealing with minor burns:
- Put water cold running water And/or a wet compress on the affected area until the pain subsides.
- if it was burn In a place where jewelry is worn (bracelet, ring, anklet), remove the jewelry immediately before subsequent swelling occurs to reduce post-burn complications.
- The blisters should remain intact. If the blisters rupture, apply antibiotic ointment immediately. If a rash occurs after using the ointment, discontinue use.
- Can be placed Cactus Or apply a moisturizer with cooling properties to the cold burn to relieve pain.
- Place a sterile bandage and gauze over the treated burn to protect the blister and prevent exposure to air that may cause pain.
- If needed, use over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief.
Treatment of sprains and spasms
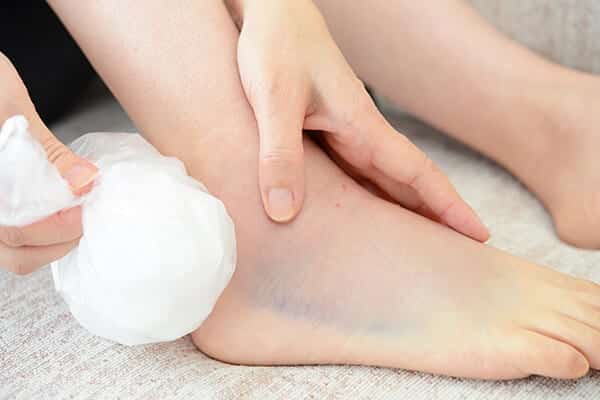

stress A sprain is a strain or tear of a ligament, while a strain is a muscle injury.
The most common sites for sprains are the ankles, wrists, knees, and thumbs. Signs and symptoms of a sprain include a popping sound at the onset of the injury, pain, swelling, bruising, and limited movement of the affected joint.
Minor sprains can be managed at home with supportive care, rest, compression, and elevation. Severe sprains may require surgical repair of the injured ligaments.
Seeking medical help for unresolved symptoms is important to improve this injury. To reduce the risk, stretching before and after any physical activity can be helpful.
Here are first aid measures for muscle cramps:
- Stretching
- massage
- Apply ice or heat
- wetting
- light exercise
- sedatives Or Pain relievers Without a prescription
- Topical anti-inflammatory creams for swelling
- Ventilation
- Seek professional help
When do you see a doctor?
A doctor or 911 should be called if a person's airway, breathing, or circulation is severely compromised. This means that a pulse cannot be felt, the person's breathing rate has decreased to zero, or the person is losing a significant amount of blood or becomes unresponsive.
last word
When providing first aid, it's crucial to remember the ABCs—airways, breathing, and circulation. Providing immediate assistance and being the first to help someone suffering from an injury or illness can help save their life, prevent further damage, and aid recovery from the injury or illness.
Having some form of first aid certification training, basic medical training, or first aid knowledge is not only ideal, but it is also helpful in identifying signs and symptoms that you may be in harm's way.
Recognizing symptoms such as sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, or loss of consciousness can help avoid potentially fatal situations. When providing first aid, you should also be aware of any potential dangers to yourself and remain alert and composed until medical help arrives.